Music Teacher Training in the Czech Republic
III. Learning and Teaching Approaches
V. Current and Future Challenges
I. Background / Organisation
The education of music teachers in the Czech Republic is differentiated according to whom they will be teaching:
· teachers for preparation of professional musicians;
· teachers of music classes at elementary and secondary schools.
The former are being educated at conservatoires and music academies. There are eight conservatoires in the CR: in Prague, České Budějovice, Plzeň, Teplice, Pardubice, Brno, Kroměříž and Ostrava. Studies last six years and the graduates from these schools can teach at state or private elementary art schools. These institutions offer specialised music education to talented children, young people and, to a certain degree, adults.
Academies of Performing Arts (one in Prague, one in Brno) are elite music colleges that produce the best professional players and composers. There are programmes to train teachers for elementary art schools and conservatories (offering secondary education), and artists with a certificate in artistic education.
Music teacher training of music teachers for elementary and secondary schools is carried out at university, Faculties of Education. There are nine in the CR – in Prague, Útí nad Labem, Plzeň, České Budějovice, Hradec Králové, Liberec, Brno, Ostrava and Olomouc.
These universities offer the following types of music teaching programmes:
· teaching music in primary-schools,
· teaching music in the secondary-schools (at most of the Faculties of Education),
· conducting children choirs and young people choirs (at most of the Faculties of Education),
· teaching in Elementary art schools (at most of the Faculties of Education).
Students following the programmes for teaching music at elementary and secondary schools usually study one more subject (Czech language, English language, German language, History, Psychology etc.) so as to be qualified to teach this alongside Music. However, they can study Music teaching in combination with another artistic specialization – conducting, playing the piano (violin, accordion) and solo singing.
Primary and secondary schools teacher trainees study for 3 years on the Bachelor programme (artistic/music performance skills, Music theory and history) – plus 2 years Master course focusing on teaching skills and pedagogical practice. In most Music Departments’ Faculties of Education, both Bachelor and Master programmes for teaching music in Elementary Art Schools are accredited, as well as programmes for conducting choirs.
The duration of the programmes (years and semesters):
· Bachelor programme (3 years = 6 semesters), Master programme (2 years = 4 semesters),
· before Lisboa and the current structuring into Bachelor and Master courses, there was also a fully-fledged Master programme lasting 4 or 5 years (8 or 10 semesters).
The quota of taught hours, study programme Music Education:
· Music teacher training Bachelor programme – a total of 741 hours (180 credits),
· Music teacher training Master programme – a total of 325 hours (120 credits).
II. Curriculum
Each music department has their own curriculum, however, the majority of subjects can be found in all study programmes. These subjects are presented in the following table.
|
Subject field |
Fields |
Obligatory |
Optional |
|
Artistic subjects |
Piano or Violin, Voice, Singing, Choir, Performance, Improvisation, Instrumental group play |
X |
|
|
Choir, Orchestra, Chamber Music, Piano for Non-pianists, Guitar or Organ, Multimedia. The number of optional subjects depends on the resources (financial and staff) of every school. |
|
X |
|
|
Music theory and history |
Solfeggio, Counterpoint, Harmony, Music-forms analysis, Music of the 20th. century, History of World Music, History of Czech Music, Music Sociology, Music Aesthetic, Ethnomusicology, Multimedia, Music and computers |
X |
|
|
Music Therapy |
|
X |
|
|
Pedagogical subjects |
Music Psychology and Diagnostics, Pedagogy with Methodology, Methodology of Music Teaching, Special Music Methodology, Teaching Practice |
X
|
|
|
Dance, Creative Music Games |
|
X |
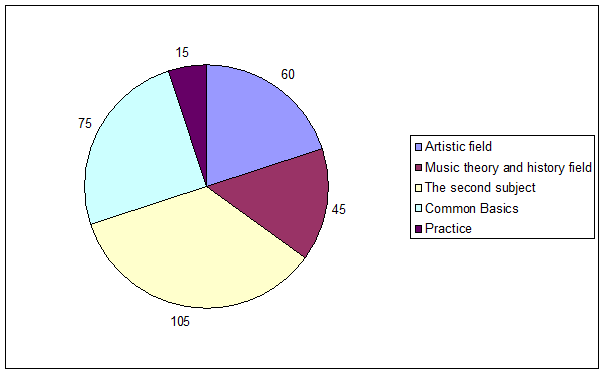
All students have the common basics – Pedagogy, Psychology, 1-2 foreign languages and Sociology. The following graph presents the relationships (the credits) between the particular fields at the Faculty of Pedagogy in the University of West Bohemia. The Music teacher training Master programmes at the others Faculties of Education differ from the one in Pilsen by approximately 20 per cent.
III. Learning and Teaching Approaches
The Music teacher training course at the Faculties of Pedagogy in CR includes different teaching and learning approaches: lectures, seminars, workshops, smaller group work, individual work, music-teaching practise, self-directed study, portfolio and e-learning.
Students’ musical interpretative growth is enhanced by their public performing within cooperation with theatres and orchestras in university towns; students perform at concerts and participate in the organisation of music and cultural events. Very talented students participate in competitions and national and international festivals and workshops. University choirs are of a high standard; they successfully represent the country at the highest international level. The academic environment provides excellent conditions for learning the basics of professional and academic work. Students can take part in research projects, test new technologies, participate int conferences and publish. Apart from music projects they learn to integrate music into community life and combine it with other fields and disciplines.
The pedagogical orientation of students is developed especially in the Master programmes. Within the general studies they acquire necessary knowledge in psychology and pedagogy, which corresponds with music psychological and pedagogical education. Teaching methodology is combined with observation practice (1 week) and then with teaching practice (2 weeks) at elementary and secondary schools as well as at elementary art schools. The final practice lasts 4-6 weeks. Students who are being prepared for a professional music career also have ongoing practice in their specific disciplines.
IV. Assessment / Examination
Usually, candidates must pass a special entrance examination. Every institution prepares its own requirements for each type of study programme. It includes:
· a written test from the basic music science,
· Music exercises (musical ear, rhythm, music memory, solfeggio)
· playing the piano or
· playing another instrument with a piano accompaniment (obligatory),
· singing without accompaniment.
The final Bachelor examination includes:
· an oral exam of the disciplines of curriculum – music theory and history,
· defence of a Bachelor thesis (min. 30 pages).
The final examination at the end of the Master studies includes:
· state finals in Pedagogy and Psychology, and in Music and the methodology of teaching music (which are oral examinations),
· defence of a Master thesis (min. 50 pages).
The title of the qualification is:
· University – BA, MA,
· Academy – BA of Arts., MA of Arts.
V. Current and Future Challenges
· There is a credit system of teaching, applied at all the universities which is, at present, very complicated and not very transparent for the students.
· The new curricular reform of primary and secondary school started in September 2007; the Faculties of Education did not have ample time to prepare for this.
· There are significant differences between music pedagogic theory and school practice.
· Information about theory and practice of music education in other countries outside the CR (books, journals) is difficult to gather.
