Music Teacher Training in Italy
III. Learning and Teaching Approaches
V. Current and Future Challenges
I. Background / Organisation
Classroom music is taught in lower secondary school (pupils aged 11-14) and in upper secondary school only in psycho-pedagogical lyceums (for pupils aged 14-19). Instrumental music is also taught in lower secondary schools and in conservatories of music.
Music teacher training for teaching in these schools takes place in universities, in “schools of specialisation for the education of secondary teachers” (SSIS) as a two year course. Training also takes place in conservatories that offer four year music education courses for both general music and instrumental teachers.
Before 2007, music teachers needed a teaching degree in order to qualify as general music teachers for lower and upper secondary schools, while instrumental music teachers only needed a degree in performance. From September 2007 all teachers of music are required to complete a second level degree (Master) in order to obtain qualified teacher status to teach in lower and upper secondary school. Since 2007/2008 the number of students entering music teacher training programmes in universities depends on the available places in each of 20 districts; and in each conservatory the maximum number of students per year is 35. Within the two year teacher training programme in universities, students have about 1000 hours of training which includes university based courses and teaching practice in schools; and teacher training courses in conservatories have about 1200 hours. Students obtain 120 ECTS credits for the qualification.
II. Curriculum
The curriculum in both types of course involves general courses in pedagogy, school legislation and management, psychology and general didactics. Specific music courses are offered in music pedagogy, music psychology, semiology and sociology of music, vocal and choral training, performance, music history, teaching improvisation and composition, and acquaintance with different musical styles. In the conservatory courses are also provided for instrumental teachers on repertoire, methodology and techniques for instrumental teaching, composing and improvising (see table 1). All students undertake teaching practice and a final thesis. In addition, there are optional courses including foreign language learning. Teaching practice is organised for each student according to general criteria. Each student has a tutor in school and a supervisor who is in charge of about 15 students.
|
General Fields |
Description |
University |
Conservatory |
|
General area of education |
basic courses for all teachers |
24 credits |
12 credits |
|
Music area |
courses for all music teachers |
|
35 credits |
|
Music: specific area |
specific courses for: music education teachers instrumental teachers |
|
40 credits |
|
Disciplinary and laboratory area: Music teaching courses |
courses only for music teachers |
24+24 credits |
|
|
Elective area (optional courses and foreign language) |
chosen by each institution |
|
12 + 3 credits |
|
Teaching practice |
|
30 credits |
12 credits |
|
Final thesis |
|
18 credits |
6 credits |
Table 1: The curriculum in universities and conservatories.
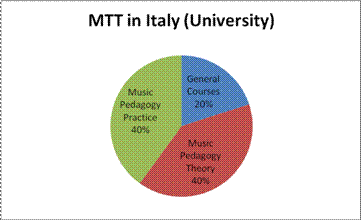
Figure 1: Distribution of credits in university based music teacher training.
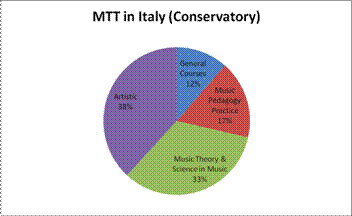
Figure 2: Distribution of credits in conservatory based music teacher training.
III. Learning and Teaching Approaches
Programmes aim to balance theoretical and practical training. The teaching skills are developed through:
· observation of experienced teachers' work during training;
· analysis and reflection upon teaching methods;
· experimentation with teaching methods, and
· consolidation of one's own practice.
Technology is used to organise lessons and as a teaching tool. Specific software programs are used for writing, composing and playing music.
IV. ASSESSMENT / EXAMINATION
The educational qualification required for entering the Music teacher training programme is a Diploma or a Bachelor’s degree achieved in a conservatory of music plus a diploma achieved in upper secondary school. A musicology degree is also accepted. Entrance exams have to be passed, according to the type of programme; for general music teacher training candidates need to pass written and oral exams, whilst for an instrumental teacher training programme, candidates need to pass musical performance and oral exams. Their acceptance is based on previous qualifications, the entrance exams and on teaching experience and their curriculum vitae.
In terms of assessment, the students have to pass an exam at the end of each course. Exams may be written or oral and for instrumental teachers they might involve musical performance. The criteria set for assessing teaching ability are set by a board made up of all the teachers involved in the programme: the supervisor for the school training (usually a teacher at a music oriented middle school), the tutor and the course coordinator. The board of examiners for each course is made up of the teacher of the course, another teacher and the director of the institution. In the final examination the board of examiners consists of two teachers, the director, the supervisor and a representative from the Ministry of Education. A teacher becomes fully qualified after passing the final exam of the programme. However, in order to be employed by the Ministry of Education and to teach in public schools, each teacher is assessed by a special board at the end of their first year of teaching in school. The university and college do not provide any further in-service training for teachers.
The final thesis in which all music teachers are assessed is based on their teaching practice; the final examination also involves the formulation of a teaching project for music teachers or performance on one’s own instrument, and conducting an ensemble for instrumental music teachers.
V. Current and Future Challenges
Although recent reform has specified that all programmes should, at first, be level (Bachelor) and second level (Master), university staff is not responsible for research and development into new teaching methods and approaches. However, within the Music teacher training course, students and teachers can apply for an Erasmus (or a Leonardo) grant and complete a teaching period for teachers or a study/training period for students.
Appendix
Table 2: Specific courses at the University and the Conservatory
|
|
Conservatory |
|
University |
|
General Area of Education: courses |
|||
|
|
12 credits |
|
24 credits |
|
General Courses |
General Pedagogy |
|
General Pedagogy |
|
|
Intercultural pedagogy |
||
|
School legislation and management |
|
History of School (with legislation and management) |
|
|
General Psychology |
|
Cognitive Psychology |
|
|
General Courses |
Psychology of Education |
||
|
|
Social Psychology |
||
|
|
Cultural Anthropology |
||
|
|
General Sociology |
||
|
General Didactics |
|
Teaching Methodology |
|
|
Music teaching courses |
|||
|
|
35 credits |
|
48 credits |
|
|
Common area for music teachers and instrumental teachers |
|
Music teaching courses |
|
Music Theory & Science in music |
Musical pedagogy |
|
Music Education: Theory and Methods |
|
Musical psychology |
|
Psychology of Music and Music development |
|
|
Composition and analysis (for music teaching) |
|
Analyses for Teaching |
|
|
Arrangement and transcription |
|
Teaching western music |
|
|
Choir and instrumental ensemble conducting |
|
Teaching Music history |
|
|
Vocal training |
Music Pedagogy |
Teaching rhythm education |
|
|
History of music (for music teaching) |
|
Teaching singing and performance |
|
|
Historical and musical research |
|
Teaching Music Listening: ethnic music |
|
|
Semiotics of music |
|
Teaching Music Listening: jazz music |
|
|
Sociology of music |
|
Teaching Music Listening: pop music |
|
|
Reading with voice and at the piano |
|
Teaching improvisation and composition |
|
|
Accompaniment |
Teaching Music informatics and electro-acoustic |
||
|
Harmonisation and transposition at the piano |
|
||
|
|
(40 credits) |
Laboratory area |
|
|
Artistic field |
Specific courses for music education teachers |
Theory and technique of music teaching in the classroom - how to schedule musical teaching |
|
|
Music Education - Methodology |
|
Laboratory for scheduling didactics |
|
|
Improvisation (for music education) |
|
Laboratory of applied teaching |
|
|
Composition (for music education) |
|
|
|
|
Choir repertoire |
|
|
|
|
Choir singing teaching |
|
|
|
|
Listening teaching |
|
|
|
|
History of Music teaching |
|
|
|
|
Music anthropology |
|
|
|
|
Body awareness and expression |
|
|
|
|
Specific courses for instrumental teachers |
|
|
|
|
Instrumental teaching – Methodology (for all instrumental specialities) |
|
|
|
|
Improvisation (for instrumental teaching) |
|
|
|
|
Composition (for instrumental teaching) |
|
|
|
|
Primary instrument, interpretation, repertoire |
|
|
|
|
Instrumental teaching – Methodology (for each instrumental speciality) |
|
|
|
|
Repertoire for instrumental ensemble |
|
|
|
|
Chamber music |
|
|
|
|
Body techniques for performance |
|
|
|
|
Optional courses |
Optional courses and foreign languages |
|
|
|
Music informatics |
|
|
|
|
Sound techniques |
|
|
|
|
Vocal improvisation |
|
|
|
|
Instrumental improvisation |
|
|
|
|
History of pop music |
|
|
|
|
History of jazz music |
|
|
|
|
Management |
|
|
|
|
Communication |
|
|
|
|
Multimedia |
|
|
|
|
Ethnic music |
|
|
|
|
Pop music – composition |
|
|
|
|
Foreign language |
|
|
|
|
|
Final exam (programme) |
||
|
|
Music teacher training: |
|
|
|
Music Pedagogy Practice |
discussion of a thesis prepared on the basis of one’s own teaching practice |
Music Pedagogy Practice |
discussion of a thesis prepared on the basis of one’s own teaching practice |
|
the formulation of a project out of three proposed by the board of examiners; it has to be done in 48 hours and then discussed with the board |
the formulation of a project out of three proposed by the board of examiners; it has to be done in 3 hours and then discussed with the board |
||
|
|
Instrumental Music teacher training |
|
|
|
|
discussion of a thesis prepared on the basis of one’s own teaching practice |
|
|
|
|
performance on one’s own instrument and conducting of ensemble (the piece of music is given 3 hours before) |
|
|
